Fistula Definition: A fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway that connects two organs or vessels that do not usually connect. They can develop anywhere between an intestine and the skin, between the vagina and the rectum, and other places. The most common location for a fistula is around the anus.
Types of Fistulas:
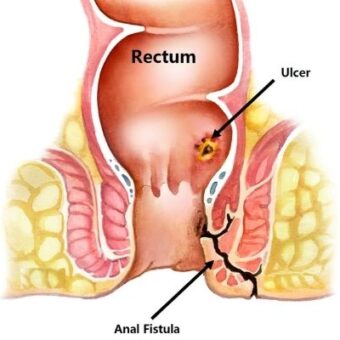
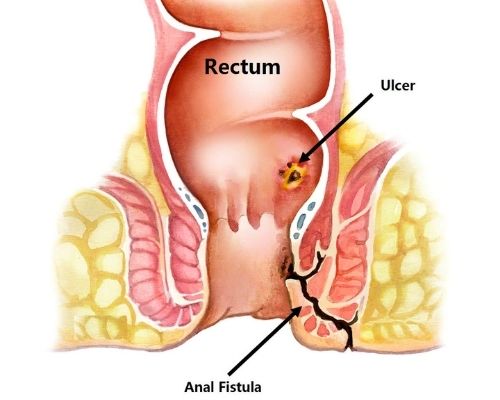
Anal Fistulas/Perianal Fistulas.
Abnormal connection between the epithelialized surface of the anal canal and the perianal skin.
- Anorectal Fistula occurs between the anal canal and the skin around the anal opening.
- Rectovaginal or Anovaginal Fistula occurs when a hole develops between the rectum or anus and the vagina.
- Colovaginal Fistula occurs between the colon and the vagina.
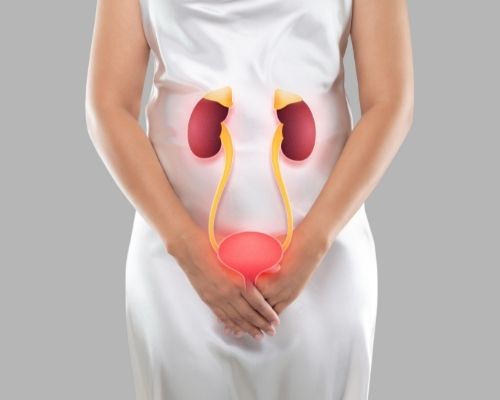
Urinary Tract Fistulas.
Abnormal openings within a urinary tract organ or an abnormal connection between a urinary tract organ and another organ.
- Vesicouterine fistula occurs between the bladder and the uterus.
- Vesicovaginal fistula is where a hole develops between the bladder and the vagina.
- Urethrovaginal fistula is between the urethra and the vagina.
Other Types.
- Enteroenteral fistula occurs between two parts of the intestine.
- Enterocutaneous or Colocutaneous fistula occurs between the small intestine and the skin or the colon and the skin respectively.
Left untreated, fistulas can be traumatic, debilitating, and can do additional harm to your body. Nerve damage, infection, and kidney failure are associated with fistulas.
TREATMENTS
Non-invasive Treatment
- Fibrin glue. A specific medicinal adhesive used to seal fistulas.
- Plug. This is usually a collagen matrix used to fill the fistula.
- Catheters. Used to drain fistulas, catheters are usually employed on small fistulas to manage infection.
Surgical Treatment
- Transabdominal surgery. The fistula is accessed through an abdominal wall incision.
- Laparoscopic surgery. This is a minimally invasive surgery that involves a tiny incision and the use of cameras and small tools to repair the fistula.
Pharmaceutical Treatment
Antibiotics or other medication may also be used to treat any infection associated with the fistula. Yet there is no pharmaceutical solution to eradicate fistulas at this time.
While fistulas pose a serious threat to your body, high treatment success should encourage you or someone dealing with fistulas to seek immediate help.